基本的な処理として。
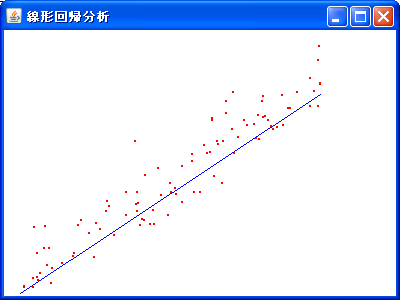
public class Regression {
public static void main(String[] args){
List<Point2D.Double> points = new ArrayList<Point2D.Double>();
double a = 10;
double b = .7;
int n = 100;
Random r = new Random();
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
double x = r.nextDouble() * 300;
double y = x * b + a + 20 * r.nextGaussian();
points.add(new Point2D.Double(x, y));
}
BufferedImage img = new BufferedImage(400, 300,
BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
Graphics g = img.getGraphics();
g.setColor(Color.WHITE);
g.fillRect(0, 0, 400, 300);
g.setColor(Color.RED);
double xx = 0;
double xy = 0;
double xt = 0;
double yt = 0;
for(Point2D p : points){
double x = p.getX();
double y = p.getY();
xx += x * x;
xy += x * y;
xt += x;
yt += y;
g.fillOval((int)x + 20, 280 - (int)y, 3, 3);
}
double rb = (n * xy - xt * yt) / (n * xx - xt * xt);
double ra = (xy - rb * xx)/xt;
g.setColor(Color.BLUE);
g.drawLine(20, 280 - (int)ra, 20 + 300, 280 - (int)(ra + rb * 300));
JFrame f = new JFrame("線形回帰分析");
f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
f.add(new JLabel(new ImageIcon(img)));
f.setSize(400, 300);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
